Alemba API Programmers’ Guide
The RESTful API is built on top of a schema that encompasses the primary data entities in the ASM System.
API structure
Additionally, a number of logical entities have been added that allow similar entities to be grouped together. The hierarchical structure allows sub-entities to inherit common properties, allowing for consistent meaning and behavior.
The structure is indicated in the Alemba API Entity Details Pane in the API explorer.
Languages
The API is platform independent - it can be accessed from any kind of web client, using a range of languages. The API Explorer provides language neutral examples of the structures sent and received as part of a web request/response, for each action, for each entity.
Authentication
The API uses standard oAuth 2.0 authentication, via /alemba.web/oauth/login.
The authentication workflow issues a short-lived (10 minutes) Access Token and a longer-lived (24 hours) Refresh Token on Login. The Access Token is used for authentication on the REST API. The Refresh Token is used to renew the Access Token and therefore maintain the session. The Refresh Token allocates a ASM Core Session and consumes a licence.
The process is illustrated as follows, flowing from the top downwards.
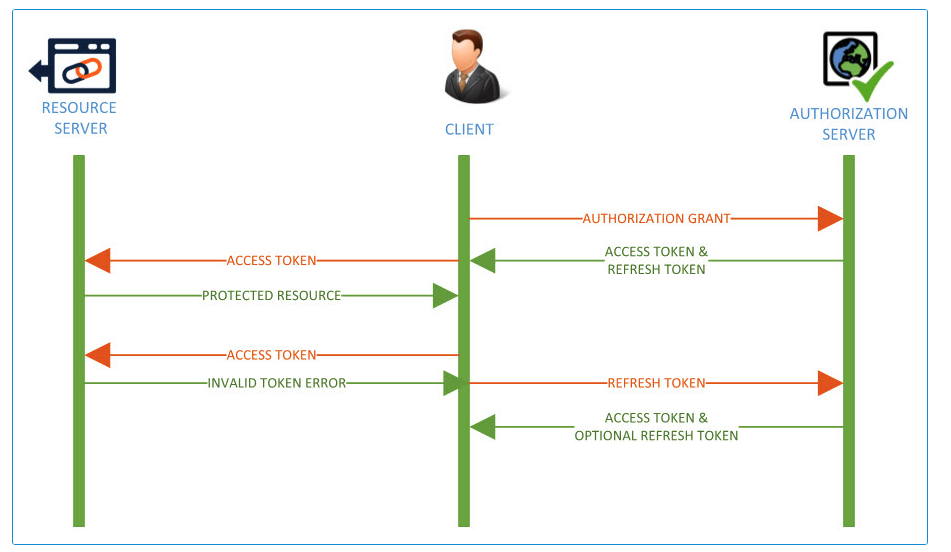
When the Refresh Token is used to renew an Access Token, a new Refresh Token is also issued, and the ASM Core Session is extended. The used Refresh Token becomes invalid and should be discarded. Clients should store the new Refresh Token for subsequent usage. If the ASM Core Session expires or is removed, the Refresh Token will become invalid. If the Refresh Token expires, the ASM Core Session is terminated.
The single use Refresh Token and short lived Access Token ensures that compromised tokens quickly become invalid - protecting the security of individual users, and preventing unauthorized Access Token reuse.
The Access Token must be presented in the Authorization header of the HTTP request:
Note that the Authorization service supports the following oAuth 2.0 Grant Types:
authorization_code – Authenticate using Single Sign On (SSO), for Windows authentication and SAML
client_credentials – Authenticate using integrated security for anonymous access to the API, not full access
password – Authenticate using a username and password
refresh_token – Authenticate using an existing Refresh Token
Logging in
UserName and Password
Below is an example of the code used to login with a username and password.
For more information on client ids, see Configuring Authentication for the Alemba API.
Access Token
Or, to refresh your access token:
scope should be set to session-type:Analyst or session-type:User. It is case sensitive.
Login Responses
For successful Logins the response will be:
Note that there is a new refresh_token in the response. The old one will no longer work and must be discarded. It is acceptable to renew your access_token before it is due to expire, but you must not do so with every request.
Login Response Errors
If the authorization request is not successful, clients can expect to receive a suitable HTTP response code and JSON formatted data containing an error code.
The response data may also include error_description, which gives the developer a clue as to the precise cause of the failure.
In these cases, the response is deliberately vague so as to protect the integrity of the authorization server.
HTTP Status Code
Error Code
Reasons
401
invalid_client
The client_id is incorrect or the client is not enabled
400
invalid_grant
The credentials are not correct, the user is not allowed to login
If you receive a 401 response, it is because your access token has expired, and you must refresh it using the refresh token. If you receive a 401 response when using a refresh token, you must login again with username and password.
Logging out
You can logout as follows:
Logout Responses
Logout will give one of the following responses:
200
Logged out successfully
400
Token invalid or missing
401
Not authorized because it’s not been possible to validate your ownership of the refresh token. In this case you must refresh the access token and try again
403
That refresh token doesn’t belong to you
404
The refresh token is valid but has already been removed. Maybe you logged in elsewhere
Base RESTful API methods
The following HTTP verbs are used by the API to perform the listed actions.
Read
GET
Update
PUT
Delete
DELETE
The API supports delete where it is appropriate, including delete for attachments and person images (avatars)
A Programmatically Discoverable API
The API can be used to return information about itself, in the form of hypermedia – machine readable descriptions and links to further similar information, allowing a developer to progressively explore the breadth and depth of the API for themselves. What is more, these descriptions are used by the API itself, guaranteeing that this “documentation” is always current.
Root Level Information on API Scope
For example, to discover root level information on the scope of the API, invoke
Note that this response will also be returned for any request which does not specify a resource, for example:
Metadata
The metadata will be returned in JSON format and will contain links to the metadata for top level entities exposed by the API, for example:
All metadata responses may include the following properties:
children
An array of descendant types for the current response
Call may list children including Incident
The metadata for each child only includes "_self"
description
A description of the current metadata response
name
The name of the entity that is the subject of the metadata response
properties
An array of property descriptions for the subject entity. These properties provide the minimum information required to understand the data model and basic constraints.
Each entry in the array may include the following properties:
name
The name of the entity property
displayName
The default display name of the property. This could be used in table column headers or form fields
type
A description of the data type of this property. The type property is a complex type which has the following properties:
displayTypes
The suggested display types for this property
dataType
The type of data this property represents
class
The kind of property
description
A description of the purpose of the property
usage
Internal when the property is used for internal business logic, otherwise Public
isKey
The property represents the unique identifier (primary key) for the entity
noSearch
When true, this property is not supported in searches
defaultValue
An indication of the default value for this property
length
The maximum length of this field. Text fields only
uppercase
When true, this indicates that the Text value will be capitalized.
Non capitalized input may cause validation errors in a future release.
status
Indicates the current release status of the subject entity. "Alpha", "Beta", "GA"
_actions
A hash map of action name and an array of action metadata
_context
A reference to the entity metadata of a record or of the metadata of the parent of the subject entity
_links
A hash map of name and an array of link metadata. These links must be requested using the http verb GET
_self
A reference to the current response link and action metadata will always include a link to _self and will often include an "href" property
HREF Templated
The "href" may be templated, as denoted by the syntax {id}. The templated values must be replaced by the client.
{id} always indicates the primary key field for the target entity. All other entity properties may also be referenced in the template. e.g. {Partition} where Partition is the name of the property in the entity referenced by "_context".
"_context" and "_self" will always define a medialink to an API resource. For brevity, the links are prefixed with "api:"
Clients should replace this prefix with the actual API base url
All API medialinks can be invoked using the $options suffix.
These links can then be followed to explore further details about the entity, what it is and what it can do.
All API entities support simple and predictable RESTful actions.
Discovering the entity actions
Many entities also support more complex actions, such as forward.
These actions are typically accessed using "api:v1/call/1/forward"
Details of the required inputs and supported HTTP method can be found in the metadata for that action.
For example the Call Create action metadata can be accessed with
http://localhost/alemba.api/api/call/$create?$options
This metadata gives you info about the Create action, including a list of mandatory and optional properties and parameters. $create in the above example can be substituted with any action that is supported by the Call entity.
What is more, you can use the same principles not just as an aid to programming, but at runtime too. The metadata that is returned about a specific object contains links for the list of actions for that object instance in its current state. (An exception is the Search action, which will only return links to the relevant Get action for each record.) For example you will only see the Reopen action if a Call is in a closed state.
Searching
The Rest API supports expressive searching of most entities
The query parameters and syntax applies to all Search actions for all entities.
To start, it is possible to simple request a resource using HTTP GET.
GET api:v1/call
This will return a reference to all accessible calls in JSON format
The response contains the following properties
"results": This is an array of search results. Each result will always include a _context url (so you know what it is) and a _self url (so you know how to get that item).
"_self": This is a url refering to the current response
Notice that the _self url includes a query string parameter
The search actually ran without any row limit. It will try to return every row (accessible to the current session).
This query string parameter is added to the response as a hint.
Paging
The Rest API supports flexible paging of search results.
$top
$top accepts a positive signed integer value (Int32) and is used to define a row count.
This will limit the response to the top 30 records. If you don’t explicitly specify the row count, then it will default to $top=100.
$orderby
$orderby accepts a comma separated list of property names and optional sort direction (see $select for more details on property names) and is used to define the order of the results
This will return all Calls ordered by Ref
By default the orderby clause will be applied in ascending order, but this can be overridden
This will return all Calls ordered by Ref in ascending order
This will return all Calls ordered by Ref in descending order
$skip
$skip accepts a positive signed integer value (Int32) and is used to define a number of rows to skip
GET api:v1/call?$top=30
This will limit the response to the top 30 records
and GET api:v1/call?$skip=30&$top=30
This will skip the first 30 records and return the next 30 (ie rows 31 to 60)
These parameters can be combined (in any order) to control page size and contents
GET api:v1/call?$top=30&$skip=30&$orderby=Ref desc
This will return the top 30 Calls ordered by Ref in descending order
$count
The API also supports counting, which can be used to calculate the total number of pages
$count must be set to true and is used to instruct the api to return a count only
This will return a text/plain response containing a number which represents the total number of rows.
$inlinecount
Alternatively, $inlinecount can be used to have the count be returned with a set of results
Note that "__count" is included in the response body.
Paging Best Practice
Use of these paging features is critical for individual client and application wide performance and should be utilized by all API consumers for all searches.
Even where it is assumed that there are only a handful of records.
Using $inlinecount results in two executions of the database query; one to get the count; and one to get the result set. Therefore it is important that this parameter is not added to every request.
Selecting columns
The Rest API supports configurable column selection in search results.
$select
$select accepts a comma separated list of property paths to include in the search results
This instructs the API to include Ref and Description in the search results
Note that as well as retrieving properties from the entity, you can directly retrieve properties from related entities. This is extremely powerful.
In the Classic WCF API, you would first need to get the raw foreign key ref from the main entity and then do a lookup on the related one, or you would have to write your own custom query, including joining objects and ensuring that the related object is not locked.
The RESTful API is built on an underlying schema that takes care of these complexities and allows you to get the data you need in the simplest possible way.
In fact you can traverse the entity relationships as far as you need, so getting a call priority’s name can be achieved with:
Linked Fields from Linked Relations
Notice that the linked entity includes metadata links. This also applies to linked fields from linked relations.
Returns
Property paths in $select can be aliased using a prefix to simplify the response
$select will also accept named Extension Augmenters
This will add the computed assignment state to the response
To help with orientation during development, $select will also accept *. This will return all properties for the entity.
Best Practice $select=*
$select=* is only intended for development and should not be used in production.
Selecting values from extension fields is supported, but carries a significant overhead and so should be avoided.
Filtering
The Rest API supports expressive filtering of search results.
$filter
$filter accepts a C# LINQ style predicate which is translated to parameterized SQL and applied as a search filter
This would return all accessible calls where the Priority is equal to 1
Equality Operators and Methods
All data types support basic equality comparison
==
Is equal to
=
Is equal to
!=
Not equal to
Binary data types support basic equality comparison but in practice, this can only be used to compare the property value with null.
Boolean data types
Boolean data types support basic equality operators
When comparing with true or false, the right hand side of a boolean property equality expression can be omitted.
Binary equality expressions can also be negated with !
is equivalent to
or
is equivalent to
DateTime data type filters
DateTime data type filters must be used with one of the applicable augmenters
This will return all Calls which were created after Midnight on January 1st 2017 (UTC+1)
Note that the date value must be expressed in ISO8601 format
@Now
The @Now augmenter can be used to compare a date value with the current time.
This is most useful where a query will be designed and then subsequently reused.
@NowOffset
The @NowOffset augmenter can be used to compare a date value with the current time and an offset expressed in days hours and minutes
This will return Calls created in the last 0 days, 1 hours and 30 minutes (in the last hour and a half).
As with all filters, the expressions can be combined using logical And (&&) and Or (||) operators
This will return Calls created between Midnight on January 1st 2017 (UTC+1) and half an hour ago.
Dates do not have to be defined in UTC format, but MUST include the timezone.
If no timezone is supplied, dates are assumed to be in local server time.
Text and RichText data types
Text and RichText data types support basic equality and can also be used with some string comparison methods
Contains
The Contains method can be used to match records where a string property contains a word or phrase
StartsWith
The StartsWith method can be used to match records where a string property starts with a word or phrase
EndsWith
The EndsWith method can be used to match records where a string property ends with a word or phrase
As with all filters, the expressions can be combined using logical And (&&) and Or (||) operators
Number Data Types
Number data types support more complex equality comparison operators
>
Greater than
<
Less than
>=
Greater than or equal to
<=
Less than or equal to
Combining Expressions
Filter expressions can be combined using logical And (&&) and Or (||) operators and can be grouped using parentheses ( and )
Note that query string parameter values must be url encoded
Sorting
$order
The API supports sorting using $order, and you can use several qualifiers, as illustrated in the following examples.
$orderby=FirstName would sort the result by the FirstName property in descending (a-z) order.
$orderby=FirstName desc would also sort the result by the FirstName property in descending (a-z) order.
$orderby=FirstName asc would sort the result by the FirstName property in ascending (z-a) order.
It is also possible to specify multiple order properties:
$orderby=FirstName, LastName asc would sort the result by the FirstName property in descending (a-z) order and then sort by the LastName property in ascending (z-a) order, e.g. Andrew Anderson, John Smith, John Jones
Joining
$leftjoin & $innerJoin
You can use $leftJoin and $innerJoin to link to entities that are not already linked as part of the schema definition. This is the case with entities that have multi-column keys e.g. CallHistory, which has a composite key of Ref and LastHistoryOrder. Once you create such a join, you will want to refer to properties of that joined entity, so part of the definition of the join is an alias for that join, in the format
… where the clause in brackets can occur multiple times. For example:
You can then use the alias in your select clause just as if it were a property of the entity with a Data Type that is the target entity, e.g. LastAction.Description.
Note that this technique should be used sparingly, because as with extension fields the relationship is not indexed and so may result in reduced performance.
Case sensitivity
Everything after any of the $ functions above is case sensitive.
Security
Handling partitions
Where entities are Partitioned, the results returned are automatically limited to those in partitions accessible to the current session. Therefore it is not necessary to apply partition filtering, however if desired, a specific partition can be specified in one of two ways.
$filter=Partition==1 will return records where the Partition Ref equals 1. The filter will be applied even if the entity is not partitioned
$partition=1 will work as above, but will only apply the partition filter if the entity is actually partitioned. This will also account for variable partitioning of Asset types, e.g api/v1/asset?$partition=1 will return a combination of Services, ConfigurationItems, etc. where Service may be partitioned, but ConfigurationItem is not.
$partition=1 is the recommended method.
Data Types
The following data types are exposed by the API:
RESTful API
Equivalent in Classic (WCF) API
Binary
Byte Array
Boolean
Boolean, Yes/No
DateTime
Date/Time
Integer
Integer
Long
Long
Float
Float
Double
Double
Decimal
Decimal
Short
Short
Text
String
RichText
String
Data types can also be entities. For example, the Service properties on a Call has a Data Type of Service (Lookup in the metadata json). This means that it contains the key value of the associated object – click on the circle icon in the API Explorer to see what that is. (This is equivalent to the WCF data type “Lookup”.)
Note that Boolean property standardizes underlying data inconsistencies. Across various tables, flags are stored as "Y", "YES", "T", "TRUE", "ON", "1", "P", "A" – for all of these, the API will return true, and conversely will convert true to appropriate values on PUT and POST.
Display Types
The following table shows the types that are supported, and the related data types.
Display Type
Data Type
Checkbox
Boolean
DatePicker
DateTime
DateTimePicker
DateTime
Lookup
entity
MultiLookup
entity
MultiSelect
entity
ListBox
entity
Numeric
Integer, Long, Float, Double, Decimal, Short
Password
Text
RichText
RichText
Select
entity
Text
Text
TextArea
RichText
TieredSelect
Entity
Augmenters
The API includes a set of inbuilt functions that simplify the retrieval of complex data using Search actions. This allows API users to easily select, view and manipulate data using business-level concepts, rather than dealing with the low level data that sometimes needs gathering from many sources to provide that information. These functions are known as augmenters. These can be used as virtual variables, for example in a filter clause. So if you only want to see calls that have breached, you would say:
There are a number of different types of Augmenters:
Condition Augmenters – for use with $filter, encapsulating complex search conditions (including joins).
Function Augmenters – provide additional functionality to the queries and are entity-independent
Token Augmenters – return simple values for use in query filters and are entity-independent
Extension Augmenters – computed properties, properties selected from other tables with join, etc.
Useful Augmenters
The table below lists some of the most useful augmenters. They are used for all entity types, and apply to calls, requests and tasks.
To find the other augmenters appropriate for an entity, examine the entity in the API explorer.
@IsDeleted
Entities that have been deleted
$filter=@IsDeleted
$filter=!@IsDeleted
@DateTime
Creates a value from a date/time string in ISO 8601 format, for use in query filters
$filter=LoggedDate > @DateTime(2000-01-01T00:00:00.000Z)
@Guid
Creates a value from a GUID string, for use in query filters
$filter=Id = @Guid(75f7a7d5-652f-4e30-bd92-dc6e9594b28b)
@Now
Current date
$filter=LoggedDate <= @Now
@NowOffset
Offsets the current date by days, hours and minutes Filter logged date within last 7 days, 2 hours, 30 minutes
$filter= LoggedDate > @NowOffset(-7,-2,-30)
@OrganizationId
Current users Organization id
$filter=User.OrganizationId == @OrganizationId
$filter=User.Organization == @OrganizationId
$filter=User.Organization.Ref == @OrganizationId
@UserId
Current user's id
$filter=User == @UserId
$filter=UserId == @UserId
$filter=User.Ref == @UserId
Error Handling
The API will return errors with an appropriate HTTP Status Code and a message with the following structure:
Type:
string - This is the type of the error – usually just the Exception type name
SubStatus:
string - This is a string which will help to narrow down the reason for the HTTP Status Code
SubStatus Values
Current SubStatus values are:
None, ResourceNotFound, RecordNotFound, LinkedRecordNotFound, NotSupported, NotImplemented, NotAllowed
Programmatically, you should rely upon the HTTP Status Code and the SubStatus.
The HTTP Status Codes that are explicitly returned are: 200, 304, 400, 401, 403, 404, 405, 415 and 500.
Often a 404 response will include a message body (as described above). This is so that you can tell the difference between a badly formed url and a non-existent record.
Was this helpful?
