Managing Tasks - Adding Tasks to the Dependency Diagram
Tasks must be created for each of the actions required to complete a request workflow. The request is considered completed when all the tasks within the request are completed.
Tasks must be created from a request. ASM provides a workflow task palette enabling you to create different types of tasks in ASM.
The ASM Workflow Polling Service must be running on the ASM server to execute any workflow-related activations.
If the workflow template you have used does not have any tasks defined, you can create your own workflow with tasks using the dependency diagram for the request:
Before you start
You can only create tasks within a workflow template, or a request. You cannot create a task independent of a request or workflow.
You must have Create Request selected in the Requests tab of your Workflow Management security role.You can only create tasks within a workflow template, or a request.
You cannot create a task independent of a request or workflow. To create tasks independent of a workflow use Call Activities.
Quick Reference
Create the request template, or view the details of an existing request.
Display the Dependencies Diagram for the request.
Add the task icon to the workflow. Drag the task type onto the workflow palette you wish to configure.
Double-click the task entity type icon. This displays the Task Details window for the selected task.
Specify the necessary information relating to the task in the Task Details window. There are some fields common to all tasks, and some are specific to the task type.
Some of the standard fields on the Task Details window described below may not appear if your system administrator has configured the screen through the ASM Designer to capture different information.
Add any other information to the task using the Task Details Explorer.
After completing the fields on the Task Details window, you can automate the following:
forward the task internally to another analyst or group for further action
forward the task to an external supplier (External Supplier Tasks only)
Deleting Tasks from the Dependency Diagram
You can delete tasks from the diagram 2 ways, from the dependency diagram and from the task itself:
Deleting Tasks Directly From the Dependency Diagram
To delete a task from the workflow, you must first delete all of its links (as of HERMES 10.6.8 build 13498).
Select the task you wish to delete.
Right-Click on the link arrow and select to Remove Link
Highlight the task again, and select the delete icon from the menu, or right-click and select to delete the task.
Deleting Tasks Using the Delete Button in the Task
Open the task
Select Delete at the bottom
Best Practices
BEST PRACTICE - Always fill out the Task Description fully.
This is very often mapped as the body of the email notification for that task so, at a minimum, you will want it to say enough to explain what the task is about and what the expected action is. It is also helpful to explain what happens next in the workflow on completion of this task. Click the image below to see an example
 .
.
BEST PRACTICE - Always fill out all of the task information.
Pay particular attention to the "Request Status on Completion", "Request Status on Rejection" and the phase and status fields. Task Type is also important.
Request Status on Completion, etc... - By understanding what the status of the request should be when the current task is finished, you can have the workflow automatically update the request to reflect it. These status are tied to request phases. You can also make use of the request status to activate rules in the screens and in the workflows.
Task Types - These indicate the nature of the task, such as UAT, Unit Testing, Development, or Delivery. As above, you can then leverage this information to enforce field rules. For example, you might want to require a test result field but only on testing tasks and no others. If you are leveraging the task type, you need not write complex rules or create numerous screens.
Task Status/Phase - This indicates where the task sits in the big picture. This is very useful for reporting and filtering.
Order - this is a way for you to create a numerical system by which you can order the tasks in task lists. e.g., 100,200,300,310,311,320,400,500... By starting with big numbers I can now see from the example above that tasks 310 and 320 are clearly part of task 300's branch. 311 would be part of 310's branch, and so on. If you do not enter an order, then your tasks will appear in lists in random or alphabetical order and it can make following the workflow more difficult.
Task Priority - some tasks are more critical than others and by setting the correct priority, analysts are better able to see them in large lists.
Planned Time - The default planned time value is 168 hours, or 7 days. If your workflow has 10 tasks, the estimated completion date could easily be several months out. If you can enter the time the task should realistically take to complete, your auto-calculated dates will be much more accurate.
FAQ
Can I make Recursive Tasks?
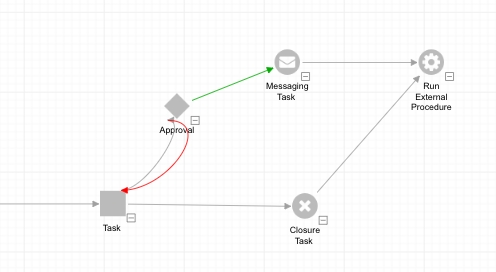
You can make any task recursive, meaning it will reopen a task that is already closed. Most often recursive tasks are approvals and Manage CMDB tasks. For example, you may have an approval for a change that if rejected, reopens the Change Review Task in order to provide an opportunity for the submitter to make changes and resubmit for approval once again. You can make a Manage CMDB task recursive so that if it fails, its preceding task, or a new task will open allowing manual intervention.
To make a task recursive, drag an arrow from it backwards to the preceding task(s). It does not have to be the task immediately preceding it.
How many tasks can I add to a request?
There is no limit on the number of tasks that you can add to a request. However, your workflow will become difficult to understand if you have too many tasks in it. Therefore, it is recommended that you split your workflow into logical units to make it easy to use.
Can I add a component workflow to dependency diagrams?
Component workflows can be added to a dependency diagram only through workflow templates. You cannot directly add a component workflow to your dependency diagram through the request.
How do I identify a component workflow in a dependency diagram?
When you create a request from a workflow template that includes a component workflow, the dependency diagram on the request displays a connector task that is linked to the tasks that constitute the component workflow. The Task Ref and Title for these tasks displays automatically in the dependency diagram from the component workflow.
Last updated
Was this helpful?
